Infrared (IR) sensors have become integral components in a wide variety of electronic devices and systems. Their ability to detect infrared radiation, which is invisible to the human eye, allows them to be used in numerous applications, from security systems to industrial automation. One specific type of sensor that is often associated with light sensing is the Light Dependent Resistor (LDR). In this article, we will explore the function of IR sensors, their different types, and the importance of LDR in sensing light.
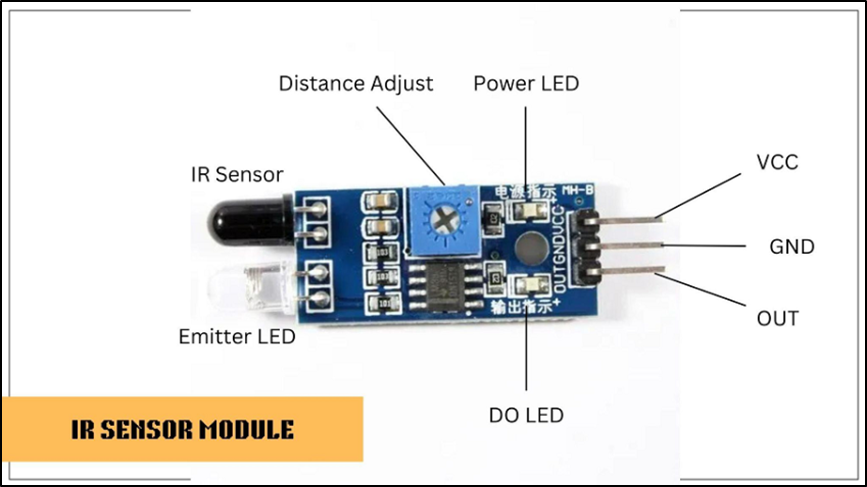
IR sensors are devices that detect infrared radiation in the form of heat or light. They function by measuring the amount of infrared light (IR) emitted or reflected by objects in their environment. The IR radiation is typically in the wavelength range of 700 nm to 1 millimeter, which is beyond the visible spectrum of light, making IR sensors ideal for detecting objects in low visibility conditions or complete darkness.
IR sensors work by emitting infrared light or by sensing the natural infrared radiation emitted by objects. These sensors convert the infrared light into an electrical signal that can be interpreted by other devices, such as microcontrollers or other electronic systems.
There are various types of IR sensors, each designed for specific applications. Below are the most commonly used types of IR sensors:
- Active IR Sensors:
- How They Work: Active IR sensors consist of both an emitter (infrared LED) and a receiver (photodetector). The emitter sends out infrared radiation, and the receiver detects the reflection of this radiation from an object.
- Applications: Used in motion detectors, proximity sensors, and object counting systems.
- Passive IR Sensors (PIR):
- How They Work: Unlike active IR sensors, PIR (Passive Infrared) sensors do not emit infrared radiation. Instead, they detect the infrared radiation emitted by objects, particularly human bodies or animals. These sensors use a special detector called a pyroelectric sensor to sense temperature changes.
- Applications: Commonly used in security systems, automatic lighting systems, and occupancy detection.
- IR Temperature Sensors:
- How They Work: These sensors detect the infrared radiation emitted by an object to determine its temperature. The amount of infrared radiation is directly related to the temperature of the object.
- Applications: Used in industrial applications, medical thermometers, and environmental monitoring.
- IR Light Sensors:
- How They Work: These sensors detect the amount of infrared light in the environment, typically from an external source, and are sensitive to changes in light levels.
- Applications: Commonly used in ambient light sensing, automatic brightness control, and night-vision systems.
Understanding Light Dependent Resistor (LDR)
A Light Dependent Resistor (LDR) , also known as a photoresistor, is a type of resistor whose resistance varies based on the intensity of the light it is exposed to. LDRs are often used in circuits that require the detection of light levels. While LDRs do not directly function as IR sensors, they play a significant role in light-sensing applications, including IR sensor systems.
- An LDR is made from semiconductor materials like cadmium sulfide (CdS) that have a high resistance in the dark but low resistance when exposed to light.
- When light strikes the LDR, photons of light are absorbed by the semiconductor material, causing the electrons to become excited. This lowers the resistance of the LDR, allowing more current to flow through the circuit.
- The resistance of an LDR is inversely proportional to the light intensity—more light results in lower resistance, while less light increases resistance.
Applications of LDR in IR Sensors
While LDRs primarily respond to visible light, they are sometimes used in conjunction with IR sensors for applications such as:
- Automatic Lighting Systems: LDRs can be used to detect the surrounding light levels and trigger IR sensors to turn lights on or off automatically based on ambient light conditions.
- Security Systems: In combination with IR sensors, LDRs can detect changes in light levels caused by motion or obstructions, improving the overall effectiveness of motion detection in security systems.
- Camera Light Sensing: LDRs are used in some cameras to adjust the aperture based on light levels, ensuring optimal image exposure.
IR sensors are used in a wide range of applications across various industries. Below are some of the most common areas where IR sensors and LDRs play a critical role:
- Security and Surveillance:
- Motion Detection: PIR sensors are widely used in security systems to detect the presence of intruders based on body heat.
- Night Vision: IR sensors help in night-vision cameras by detecting infrared radiation from objects, even in complete darkness.
- Industrial Automation:
- Object Detection: Active IR sensors are used in conveyor systems to detect the presence or absence of objects, ensuring smooth automation processes.
- Temperature Monitoring: IR temperature sensors monitor machinery to prevent overheating and damage, improving the safety of industrial systems.
- Consumer Electronics:
- Remote Controls: Many consumer electronics, such as televisions and air conditioners, use IR sensors to receive signals from remote controls.
- Smartphones: IR sensors help in proximity detection for screen dimming or enabling features like face recognition.
- Medical Devices:
- Non-contact Thermometers: IR temperature sensors are used in medical devices to measure body temperature without requiring direct contact, crucial in infection prevention.
- Automotive Industry:
- Night-vision Cameras: Some vehicles are equipped with IR sensors that help drivers see objects on the road in low-light conditions.
- Non-contact Detection: IR sensors, especially PIR sensors, offer the advantage of non-contact detection, which is useful for situations requiring hygiene or safety.
- Low Power Consumption: Most IR sensors, including LDRs, consume very little power, making them ideal for battery-operated systems.
- Versatility: IR sensors are used in a wide range of applications, from simple motion detection to complex temperature measurement systems.
- Sensitivity: IR sensors are highly sensitive and can detect even small temperature variations or minute changes in light.
IR sensors are powerful tools for detecting infrared radiation, enabling a wide range of applications in security, industrial automation, consumer electronics, and more. When combined with components like LDRs, these sensors become even more versatile, capable of detecting light levels and providing useful data in various environmental conditions. Understanding the principles behind IR sensors and LDRs helps engineers design more effective systems that improve efficiency, safety, and functionality across multiple industries.
By harnessing the power of both IR and light sensors, businesses and individuals alike can optimize their devices and systems for smarter, more responsive operations.

